Karpenter Kubernetes Node Autoscaling
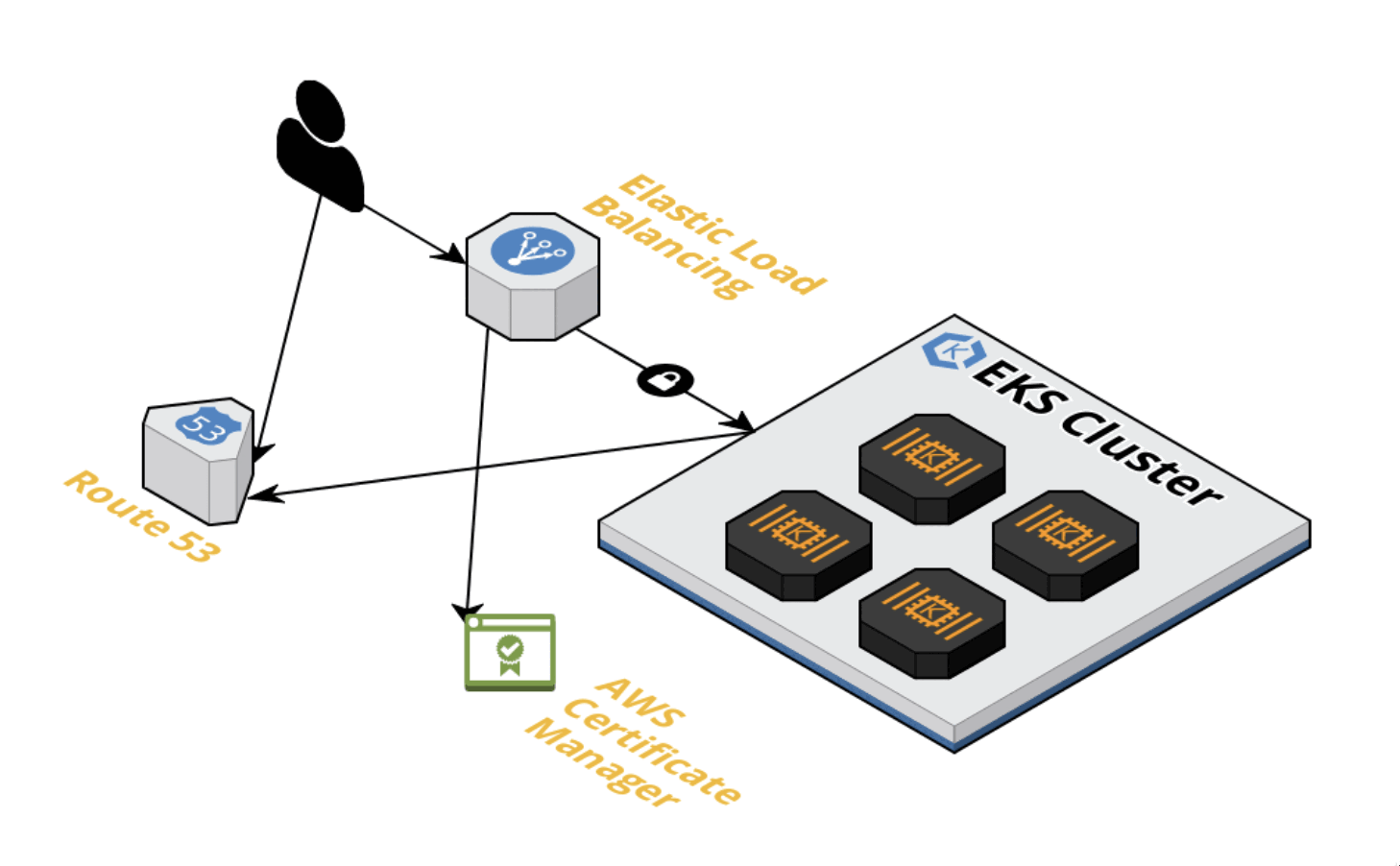
K8S Autoscaling helps us to scale out or in our applications. Pod-based scaling or HPA is an excellent first step. However, the problem is when we need more K8S nodes to contain our PODs. Karpenter is a Node-based scaling solution built for K8S, and its goal is to improve efficiency and cost. It is a great solution because we don't need to configure instances types or create nodegroups, which drastically simplifies configuration. On the other hand, the integration with Spot instances is painless and we can reduce our costs (up to 90% cheaper than On-Demand instances)
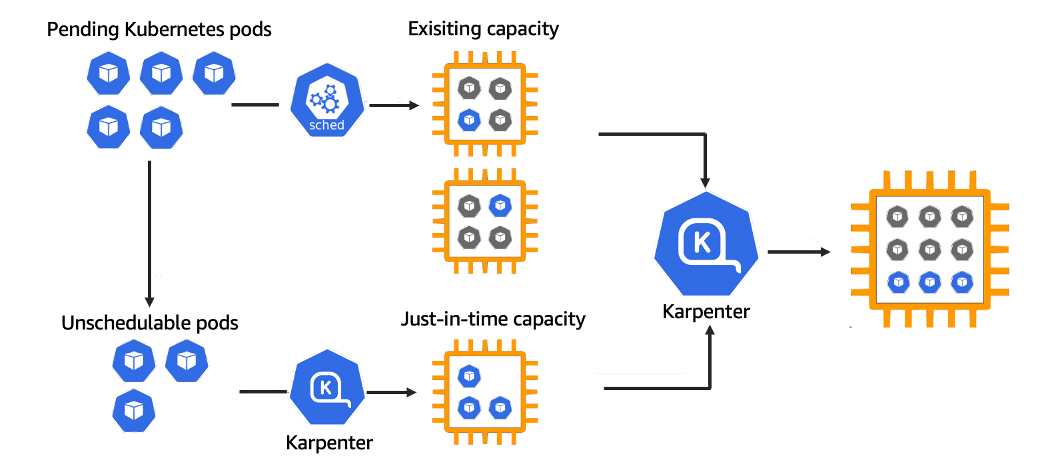
A Kubernetes node autoscaling solution is a tool that automatically adjusts the size of the Kubernetes cluster based on the demands of our workloads. Because of this, we don’t need to create manually a new Kubernetes Node every time we need it (or delete it). Karpenter automatically provisions new nodes in response to unschedulable pods. It does this by observing events within the Kubernetes cluster, and then sending commands to the underlying cloud provider. It is designed to work with…